Analysis 13: Company Role Reasons
EXHIBITS:
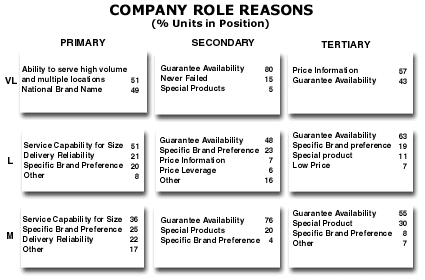
| HOW TO INTERPRET THE ANALYSIS: This company was chosen by its customers for multiple reasons in every Role. For example, in the Very Large customer/Primary Role position, the company was chosen for two reasons. First it has the ability to serve high volume customers in multiple locations. In other words, the company is able to deliver product in a large geographic area and to meet the needs of the largest customers in the marketplace. The company got 51% of its sales because of its ability to serve these larger customers. Second, the company received 49% of its total sales in the Very Large/Primary position because of its national brand name. This means that the company had a well-known brand name that caused customers to ask for the company's brand as they shopped.
PURPOSE: It is common for a company to be chosen by customers for specific reasons to fill various positions in the marketplace. This analysis enables the company to see the reasons why it is chosen over others by the marketplace. These reasons are strengths compared to others and attributes that the company may develop with other customers. APPROACH: The company obtains this information by (1) a thorough debriefing of the sales force responsible for customers in each size category and (2) customer interviews. The basis of the 100 in each position is the total sales the company has by position (that is, the combination of customer size and role). The volume behind each reason in the position is divided by the total volume in the position to arrive at the percentage by reason. |
|
Recommended Reading |
| For a greater overall perspective on this subject, we recommend the following related items:
Analyses: Symptoms and Implications: Symptoms developing in the market that would suggest the need for this analysis.
Perspectives: Conclusions we have reached as a result of our long-term study and observations.
|
