Innovation for Customer Cost Reduction
Four Price Points
Capsule: You should group all the market’s products, both yours and those of the competion, into Price Point types, which are combinations of performance and price: Standard Leader, Performance Leader, Price Leader and Next Leader. Then determine the market shares and growth rates of each Price Point.
For helpful context on this step:
Videos:
- Video #69: Overview of Products and Services Part 1: How to Look
- Video #23: Full Explanation of Price Points and Competitor Types in a Market
- Video #78: Competing Against Low-End Competition Part 1
- Video #79: Competing Against Low-End Competition Part 2
- Video #19: Definition of Standard Leaders
- Video #20: Definition of Performance Leaders
- Video #21: Definition of Price Leaders
- Video #22: Definition of Next Leaders
- Video #24: Price Point Specialists in Hostility
Perspectives:
- “Attention K-Mart Copiers”
- “Patterns of Product and Service Innovation”
- “Success Under Fire: Policies to Prosper in Hostile Times”
- “The Choice of New Products”
- “Turmoil Below: Confronting Low-End Competition”
- “When Product Mix Matters”
- “Why Do Leaders Lead?”
Symptoms and Implications:
- New entrants are growing much faster than the market
- Low end products are gaining share of the market
- One or more companies have introduced a better product at a lower price
- Price points are growing at differential rates as companies enter higher end niches to improve profits
Value is the combination of the performance each supplier offers the customer and the price the supplier demands for that performance. Generally, increases in performance raise the cost of a product so the performance and price components of value usually move in tandem. Each competitor in an industry develops as one of four Price Point specialists. Each company must make tradeoffs to balance performance and price in the value it offers customers. The first place this tradeoff occurs is in the choices a company makes to offer Price Points.
The first Price Point specialist, a Standard Leader, offers the industry’s most common products, with average performance and prices. Two other Price Point specialists follow contrasting paths in offering customer value. Performance Leaders offer products with above standard performance in return for higher than standard prices. Price Leaders offer prices well below standard for products with lower than average performance. Finally, some industries produce Next Leaders. These fortunate companies offer a niche segment of customers better than average performance for lower than standard price. Of the four types, Standard Leaders are the most common and command the greatest share of an industry’s market.
See a “Leader’s Comparison” Chart >>
The Price Point classifications apply at the product level as well as at the company level of competition. Every product, as well as every company, fits one of the Price Point classifications. Each of the four types of Price Point specialists has the potential to offer products to compete with other Value Leaders. For example, Standard Leader Toyota offers a Performance Leader line of automobiles with the Lexus brand. Standard Leader Marriott International competes at the Price Leader end of the lodging industry with its Fairfield Inn product. Standard Leaders can, and often do, offer products to compete with all three of the other Value Leaders. Performance Leaders and Price Leaders may also offer products in other categories, especially in the Standard Leader category.
Examples of Industries With Four Price Points »
Standard Leader. There are three types of Price Point that are common in markets and one more that appears only on occasion. This first type is the Standard Leader. The Standard Leader products set the bar for performance and price in a marketplace. The most common product in the market is the Standard Leader product. This product serves as the reference point for the evaluation of all other products in the market. Standard Leader product examples would include standard branded disposable diapers, a 12 oz. can or bottle of “premium” beer, a standard overnight air-express delivery, R-19 Kraft-faced home insulation, and a supermarket. The term Standard Leader refers not only to products but also to the companies whose major product emphases are on Standard Leader products. Examples of these Standard Leader companies would include Procter & Gamble, Anheuser Busch, Federal Express, Owens-Corning, and Kroger. Each Standard Leader company would have Standard Leader products accounting for a percentage of sales within ten percent of the industry average. If the industry received 75% of its revenues from Standard Leader products, each Standard Leader company would derive at least 65% of its sales from Standard Leader products.
Performance Leader. The second type of Price Point, Performance Leader, sits at the high-end of the product price and performance range. These products offer more benefits for higher prices than do the Standard Leader products. Examples of Performance Leader products include first class airline travel, combination PDA phones, specialty beers, and laptop computers. The term Performance Leader can also refer to those companies that specialize in selling products at the higher end of the product marketplace. These companies would include BMW, Nordstrom, Restoration Hardware, and Bose. Each Performance Leader company would gather at least 50% of its revenues from Performance Leader products.
Price Leader. The third type of Price Point, Price Leader, occupies the lower end of the price and performance spectrum. Price Leader products offer less performance in return for a low price. Price Leader products would include entry-level personal computers, small automobiles, and most categories of private label products. Price Leader specialist companies include Costco, IKEA, Drypers, and Alamo Rent-a-Car. Each Price Leader company would generate at least 50% of its revenues from Price Leader products.
Next Leader. In a few markets, there exists a fourth category of Price Point, Next Leader. Next Leader products offer a segment of the market better performance for a lower price than is standard. This fortuitous combination seems implausible. But these products, and the specialist companies that produce them, have a uniquely low cost system behind their high performance and low prices. The Next Leaders often remove some benefits and add back others to produce their better performance, as well as a part of their low cost structure, for a segment of customers in the marketplace.
There are two primary types of Next Leader: Reformer and Transformer. A Reformer Next Leader reduces Function benefits but offers some new Convenience benefits for the buyer. An example is Amazon.com, which removes some of the amenities of the traditional bookstore, but provides the convenience of buying books and other products from any computer at any hour with the click of a mouse. A Transformer increases Function benefits, sometimes at the expense of Convenience benefits. Category killer retail stores, such as Home Depot, offer customers far more product choice than their Standard Leader competitors, while opting for less convenient locations and less service, both Convenience benefits, to keep their costs and prices low. Next Leader companies often quickly become Standard Leader companies in new industries. Past Next Leader Companies have included such companies as Cisco Systems, Blue Mountain Arts, and Jiffy Lube.
Four Price Points Questions
| | Analysis 38: |
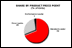
| | Analysis 39: |
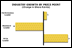
| | Analysis 40: |
- What is the most common, or Standard Leader, product sold in the market place? (Analysis 38)
- What Price Points exist above and below this Standard Leader product? (Analysis 38)
- What percentage of the industry’s total volume is sold at each of these Price Points? (Analysis 39)
- What is the leadership type of each competitor in the market?
- What are the growth rates of the various Price Points? (Analysis 40)
- How do those Price Point growth rates compare to the average growth of the industry as a whole? (Analysis 40)
- Why are there differences in Price Point growth rates from the industry average?