BASIC STRATEGY GUIDE: STEP 3
Activity One (Steps 1-12):
Segment customers, both by size and by need, to identify targets for the Company.
Step 3: Understand the size and purpose of multiple roles in customer relationships.
What:
Determine how many suppliers the average customer in each size segment uses to meet its needs. Find the reasons for the Supplier Roles other than the Primary Role.
Purpose of Roles: Industry Examples »
Why:
This step prepares for a further size segmentation of customers. When customers buy from several suppliers, the amount of purchases they make from each supplier varies significantly. When we calculate the economic worth of a customer to the company, the real “size” of the customer is the amount the customer will purchase from the Company, not the total purchases of the customer.
What to Watch For:
-
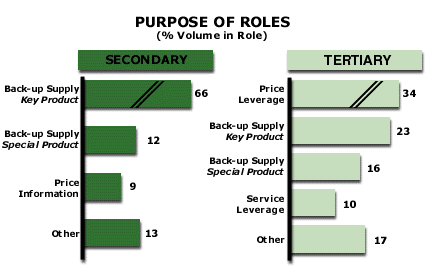
More than one Supplier Role implies a failure of some kind by the Primary suppliers.
-
The Secondary supplier usually offers one of the following benefits:
-
Backup supply to ensure availability
-
Service or Price information
-
A special product not carried by the Primary supplier
-
-
Tertiary suppliers usually exist for one of the following reasons:
-
Special products not carried by the Primary or Secondary suppliers
-
Audio Tip #12: Supplier Roles and the Customer Buying Hierarchy
Action:
Consider the roles the Company can fill. The strategic roles in any customer relationship are always the Primary or the Secondary roles. The Company should determine the customer size segments where it comfortably fills either of these roles.
More Information on the Size of Roles on the Advanced Site
More Information on the Purpose of Roles on the Advanced Site
For helpful context on this step:
Videos:
Perspectives:
Symptoms and Implications:
