BASIC STRATEGY GUIDE: STEP 25
Activity Four:
Manage the Company’s cost structure to create economies of scale while offering good value to Core customers.
Step 25: Evaluate the Company’s advantages or disadvantages in visible costs compared to low-cost competitors.
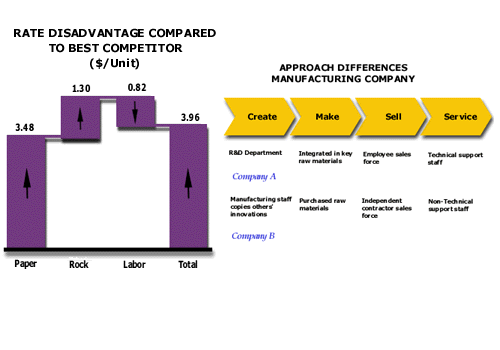
In the previous step, you set your return on investment targets and analyzed the gap you have to close to reach that target. Part of the gap may be due to cost disadvantages that you have compared to competition. Two of these cost disadvantages are usually visible and easy to analyze. The first is a disadvantage in rates of cost paid for people, purchases or capital, especially for people and purchases. The second is a difference in approaches the Company uses to manage functional costs. In this step, you will evaluate these visible cost disadvantages and form a plan to address them.
What:
Analyze the Company’s visible cost disadvantages. First, compare the Company rates of costs for key purchased items and key components of labor against the rates of the low cost competitors. Second, compare the Company’s approach to managing the important cost functions of its business to those of its key low-cost competitors. These comparisons should explain major variations in product unit costs due to rates and approaches.
Why:
In “commodity” industries, where sales, general, and administrative expenses are below 10% of sales, the rates of costs the Company pays, compared to its competition, may determine its long-term ability to compete in the market place. In most markets, significant new approaches to managing a key functional cost may signal a widespread cost reduction coming in the industry and the opportunity for the Company to adopt this new low cost approach early.
What to Watch For:
The key cost management issue for the company is to maintain control of the customer relationship. This means the company must control the marketing and sales functional costs. Other functional costs are less critical.
- Audio Tip #180: The Real Low-Cost Competitor
Rate advantages and disadvantages occur in cost functions of many companies. Most of these rate differences are the result of four key drivers: the source of purchases, the size of the purchases, the timing of the purchase and the components of the rate itself. More Information>
- Audio Tip #176: Causes of Advantages in Rate of Cost
Differences in approaches to managing a functional cost are commonly the result of a decision either to have a third party conduct part or all of the functional cost or to employ a different technology in the cost function.
- Audio Tip #178: Typical Cost Functions for Manufacturing Businesses
-
Audio Tip #179: Typical Cost Functions for Wholesale, Retail or Distribution Business
- There may be different approaches to functional cost management used to serve different sized customer segments, that is, the Very Large, Large, Medium and Small customers. In that case, the Company needs to track approach differences in each of the segments where it wishes to compete.
Any new approach to managing functional costs that is growing rapidly in the market is likely to become the industry standard approach. More Information>
Action:
Evaluate the sustainability of either the Company’s advantages or disadvantages in rates paid for key cost elements and then adjust the rate of the Company’s investment in the industry accordingly.
Test Your Knowledge: Sources of Cost Advantage>>
- Self Test #25: Evaluate the Company’s Advantages or Disadvantages in Visible Costs
Worksheet #25: Evaluate the Company’s Advantages or Disadvantages in Visible Costs
More Information on Matching Competitive Cost Advantage on the Advanced Site>>
For helpful context on this step:
Videos:
- Video #24: Price Piont Specialists in Hostility
- Video #51: Alternatives for Functional Cost Management in Hostility
Perspectives:
Symptoms and Implications:
