BASIC STRATEGY GUIDE: STEP 18
Activity Two (Steps 13-18):
Develop new products and services to gain share with Core Customer segments.
Step 18: Modify the Company’s product and service innovation program to reflect the worth to the company and the praticality of each innovation.
What:
Rank potential product and service innovations both by value to the company and by the ability of the company to implement the innovations.
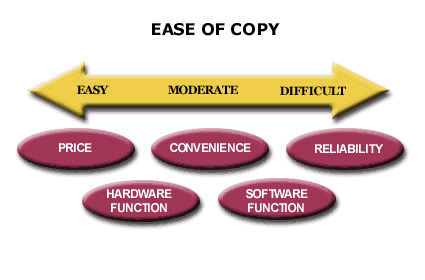
An important consideration in the value of an innovation for the company is the ease with which a competitor might copy the innovation.
The Company should review the history of how long previous innovations remained unique. More specifically, the Company should determine how robust previous categories of innovation have proven to be.
-
Each innovation falls into one of the categories of the Customer Buying Hierarchy: Function, Reliability, Convenience, and Price.
-
Customers purchase from a supplier because they view the supplier as unique on some benefit. In this case, “unique” means less than half the current suppliers offer the particular benefit.
-
The objective of the product and service innovation program is to create uniqueness for the Company with its core customers so that they will increase their purchases from the Company.
-
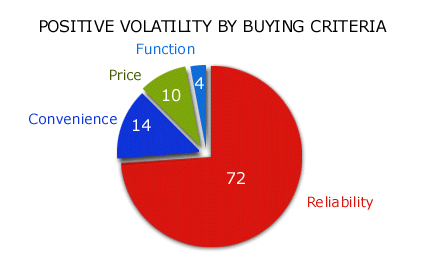
The history of innovations on the Customer Buying Hierarchy gives an indication of where the industry has been most successful in creating uniqueness. This history of unique benefits is reflected in the purchasing patterns in the industry’s positive volatility. Those categories (i.e., Function, Reliability, Convenience or Price) on the Hierarchy with the greatest customer purchase volume are those that competitors find most difficult to copy.
Positive Volatility by Buying Criteria: Industry Examples»
Why:
The Company, in its value innovation program, must find an appropriate balance between value for the customer and profit for the company. Basic Strategy Guide Step 17 ensured that the potential innovations had value for the customer. This step assesses the attraction of each potential innovation to the company. A performance innovation that the industry competitors may copy quickly offers the Company virtually no uniqueness in the market place and is unlikely to improve the Company’s market share. The Company should implement those potential innovations that assure it of profits and that the Company can implement practically in the future.
What to Watch For:
-
Developing and many Stable industries will often see high levels of Positive Volatility on both Price and Function. As industries mature, and especially when they become Hostile, Function innovations tend to be copied quickly and offer only short periods of uniqueness.
-
Deteriorating industries often have high Positive Volatility on price as one or several industry leaders fall into the Leader’s Trap.
-
In all types of markets, customers new to a market are strongly influenced by product differences in function and price. In contrast, established customers buy overwhelmingly on Reliability and Convenience.
-
Once the industry is established and out of its high growth period, virtually all strong Standard Leaders gain and hold their market shares primarily due to Reliability and Convenience.
-
An innovation may not make the Company unique or increase current share, but may become necessary to avoid failure in the customer’s eyes.
Action:
Use the perspectives of an innovation’s net value to the company and near-term practicality of implementation to set final priorities for the product and service innovation program.
-
Self Test #18: Developing Priorities for Product and Service Innovations
-
Worksheet #18: Developing Priorities for Product and Service Innovations
More Information About the Customer Buying Hierarchy on the Advanced Site >>
More Information About Benefit Duplication on the Advanced Site >>
More Information About Value for the Company and the Customer on the Advanced Site
>>
More Information About Capacity for Innovations on the Advanced Site >>
For helpful context on this step:
Videos:
-
Video #27: Full Description of How the Customer Buying Hierarchy Works
-
Video #70: Overview of Products and Services Part 2: What to Expect
-
Video #71: Overview of Products and Services Part 3: What to Do
-
Video #34: Types of Product Innovations That Reduce Customer Costs
-
Video #36: Probable Priorities for Innovation in Hostile Markets
Perspectives:
Symptoms and Implications:
