BASIC STRATEGY GUIDE: STEP 14
Activity Two (Steps 13-18):
Develop new products and services to gain share with Core Customer segments.
Step 14: Determine the reasons for the Company’s “hidden” Negative Volatility
What:
Evaluate all reasonably available instances of hidden negative volatility among the Company’s core customer segments to understand the specific reasons that the customer did not choose the Company.
The Company has sources of negative volatility that are often hidden from it. This negative volatility is hidden because it does not occur when a customer reduces his purchases from the Company. Rather, it occurs when the Company: is not invited to bid for the customer’s purchases (invitation failure), or loses in the customer’s evaluation process (evaluation failure). The easiest form of this hidden negative volatility to track is evaluation failure, where the Company loses out in final competition with other competitors for the customer’s volatile volume. The Company should estimate the volume opportunities it loses due to evaluation failure.
The Company may find it helpful to classify each reason for the Company’s hidden volatility with core customer segments into one of the four categories of the Customer Buying Hierarchy. This latter step gives the Company a broad understanding of its reputation with those customers in the market place who choose not to use the Company in their relationships.
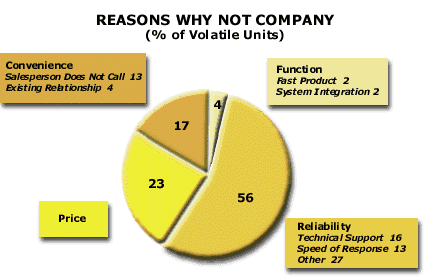
Reasons “Why Not” Company: Industry Examples»
Why:
The reasons for hidden volatility in evaluation are shortcomings in the Company’s package of products and services currently offered to the market place. Most, if not all, of these shortcomings represent “Failures” in the eyes of the customers. By eliminating these “Failures,” the Company has immediate access to some amount of positive volatility without having to invest first in innovations that are entirely new in the market place. The reasons for hidden volatility in invitation may reflect an outdated understanding of the company’s current performance.
What to Watch For:
-
Invitation failure is usually greater than evaluation failure. Both failures indicate problems or opportunities for the company. Invitation failure may be due to a reputation among some customer segments as a result of company actions and decisions from several years ago.
-
In a Hostile market, the company should not have invitation or evaluation failures due to price among current or potential Core customers.
-
The company’s percentage failures on Reliability should be below those of the industry as a whole.
Action:
Develop specific innovations to eliminate the major reasons for the Company’s hidden negative volatility with its core customer segments.
-
Audio Tip #68: Producing a Net Value Improvement for Customers
-
Self Test #14: Identifying Reasons for “Hidden” Negative Volatility
-
Worksheet #14: Identifying Reasons for “Hidden” Negative Volatili
More Information on Hidden Negative Volatility on the Advanced Site>>
For helpful context on this step:
Videos:
Perspectives:
Symptoms and Implications:
