Analysis 9: Purpose of Roles Other Than Primary
EXHIBITS:
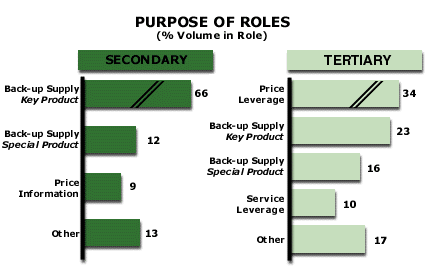
| HOW TO INTERPRET THE ANALYSIS: In this industry, there are two Roles in addition to the Primary Role in the average customer relationship. The exhibit shows the reason for each Role, along with the percentage of the volume in the Role that is associated with each reason.
The volume in the Secondary Role in the industry represents all the sales that suppliers in the Secondary Role in the customer relationship sell to all customers in the market. The sum of the bars is 100%. 66% of all the sales by Secondary suppliers to customers are made in order to provide those customers with backup supply on the key product the customer buys. This back up supply insures the customer that he will be able to get the product even if the Primary supplier is unable to deliver that key product. 12% of the volume sold by Secondary Role suppliers to all customers in the marketplace is there to provide the customer with back up supply on a special product. These special products are less important to the customer than the key product. This Secondary Role supplier volume is there to insure the customer that he will be able to get his special product even if the Primary supplier is unable to deliver it. The set of horizontal bars on the right hand side of the exhibit represents the reasons for the existence of Tertiary suppliers. The sum of the bars is 100%. Tertiary suppliers are those industry competitors who rank third in customer relationships in the industry's total sales. The bars represent the percentage of all sales by Tertiary suppliers that is associated with each reason for the Role. 36% of all Tertiary supplier sales to customers provides the customer with price leverage. Price leverage allows the customer to use the low price of the Tertiary supplier to convince his Primary and Secondary suppliers to reduce their prices. 23% of the total sales of the Tertiary suppliers in the market provide back up supply to the customer for the customer's key product in the marketplace. This arrangement insures that customer that he will be able to receive his key product even if the Primary and the Secondary supplier are unable to deliver the product. PURPOSE: This analysis helps the company understand why a customer would need to have more than one supplier in his relationship. Purpose of Roles: Industry Examples »
APPROACH: Through the sales force, the company can estimate the reasons, and the importance of those reasons, for other roles besides the primary role. If the company has a good sample and good insight into how customers think, it can develop percentages of volume attributable to each reason. If not, the company can estimate the priority of these reasons to establish a ranking. A company in a primary role relationship with the customer would try to alleviate the problems implied by the customer's needing to have secondary and tertiary suppliers. If it can ease these problems, the company might take over more of the customer's relationship. On the other hand, a follower company would seek to exploit these reasons and problems in order to get into a customer relationship and build upon it from something other than the primary position. Each role reason implies that the supplier in the role above the role being examined could not, or would not, offer this benefit to the customer. For example, a customer seeking a back-up supplier in a secondary role position is signaling that his primary supplier has not given him enough assurance that the supply will always be available when the customer needs it. Roles that are secondary and below always imply a shortcoming in the benefits offered by the primary supplier. In order to be most effective, the statement of these shortcomings should be as concrete as possible. For example, a customer may cite “responsiveness” as the reason he uses a secondary supplier. The company will be better able to take action to gain share in the secondary role or to protect share in the primary role if it defines "responsiveness," for example, "three-day order cycle time on special orders" or "willingness to add features to a standard product". |
|
Recommended Reading |
| For a greater overall perspective on this subject, we recommend the following related items:
Analyses: Symptoms and Implications: Symptoms developing in the market that would suggest the need for this analysis.
Perspectives: Conclusions we have reached as a result of our long-term study and observations.
|
