Analysis 57: Cost Advantages and Disadvantages Due to Differences in Approach to Managing Functions
EXHIBITS:
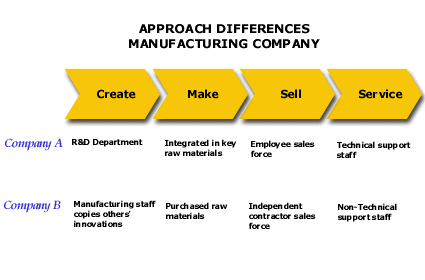
| HOW TO INTERPRET THE ANALYSIS: Company A and Company B pursue entirely different approaches to the functions of Create, Make, Sell and Service of the product. In the Create function, Company A uses its own research and development department while Company B copies other companies' designs. In the Make function, Company A is fully integrated in key raw materials, which means that it owns its own source of raw materials, whereas Company B purchases raw materials from the outside. The remainder of the exhibit is self-explanatory. The major difference between the two companies is that Company A does most of the work in every function itself where Company B outsources to third parties wherever possible.
PURPOSE: This analysis helps the company determine whether to change the functional approaches it is using to deliver its product/service package to its customers. APPROACH: Each competitor in the marketplace employs a particular functional approach to serving his chosen customers with his value proposition. Any differences in functional cost approaches from one competitor to another can create cost advantages or disadvantages. This analysis is meant to lay out the differences in approaches that the best (i.e. lowest cost) competitor employs and then to quantify those different approaches into a unit cost advantage or disadvantage for the company, relative to its best competition. Marketing, sales and operations lay out the differences in the approaches used by each competitor. Finance then helps each group determine the cost advantage or disadvantage the company has compared to the best competitor in the industry.
Return to Diagnose Costs: Approaches to Managing Functional Costs |
|
Recommended Reading |
| For a greater overall perspective on this subject, we recommend the following related items:
Analyses: Symptoms and Implications: Symptoms developing in the market that would suggest the need for this analysis.
Perspectives: Conclusions we have reached as a result of our long-term study and observations.
|
