Analysis 38: Definition of Price Points in the Market
EXHIBITS:
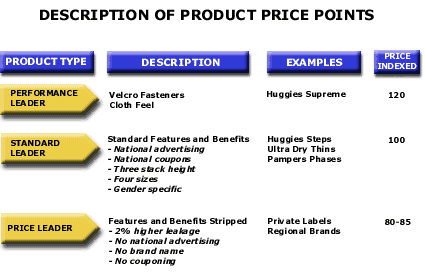
HOW TO INTERPRET THE ANALYSIS: This exhibit portrays three Price Points in the market. The first column names the Price Point. The second column lists the benefits of the Price Point. The third column lists some of the competitors' products at each Price Point. And the final column shows the price of each product indexed to the Standard Leader Price. The Standard Leader product in the marketplace would be represented in this market by Huggies Steps and Pampers Phases. Each of these products would have, as standard benefits: national advertising, national couponing, three stack height, four different sizes and gender specific diapers. At the higher, Performance Leader, Price Point are Huggies Supremes, at a 20% price premium over the Standard Leader product. For that price premium, this product offers Velcro fasteners and a cloth feel.
PURPOSE: This analysis groups price points in the marketplace according to their price and benefit levels. It is the first step in the company's evaluation of the profitability and growth rate of product types in the market and in its subsequent decision on whether to offer particular price points. APPROACH: The Performance Leader price points are those offering higher performance for higher price than the industry average. Standard Leader price points offer the industry standard performance and price in the marketplace. The Price Leader price points are those products that have a lower price and lower level of benefits than the standard in the industry. A Next Leader price point may also exist in some industries. These products offer a performance level that is better than standard for a niche segment of customers in the marketplace. Next Leader product prices are usually lower than the standard price in the market. Many industries will have Performance, Standard and Price Leader products. Few industries will have Next Leader products. The Standard Leader product is that which sells the highest unit volume in the marketplace. That product need not be the majority, that is, more than 50% of the units sold in the marketplace, only the product with the highest number of units. In most industries, those products priced within 7% of that standard industry price are also Standard Leader products. Performance Leader products offer more benefits for prices beginning about 7% over the Standard Leader products. Price Leader products offer substantially fewer product benefits for much lower product prices.
Examples of: |
|
Recommended Reading |
| For a greater overall perspective on this subject, we recommend the following related items:
Analyses: Symptoms and Implications: Symptoms developing in the market that would suggest the need for this analysis. Perspectives: Conclusions we have reached as a result of our long-term study and observations.
|
