BASIC STRATEGY GUIDE: STEP 11
Activity One (Steps 1-12):
Segment customers, both by size and by need, to identify targets for the Company.
Step 11: Classify and assign a Company objective to each current and potential customer
What:
Place each current and potential customer into one of three categories:
-
Core customers: customers with whom the Company will earn its cost of capital through the business cycle
-
Near-core customers: customers with whom the Company will maintain or establish a relationship in the expectation that the customer can be turned into a Core customer. These customers earn a positive return on investment but a return below the Company’s cost of capital.
-
Non-core customers: customers with whom the Company would do business only during periods of overcapacity. Sales to Non-core customers produce cash for the Company but do not produce any return on investment on the sale. The Company would not add capacity to support these customers. As its industry emerges from overcapacity, the Company would use the volume sold to these non-core customers to support the growth of its core customer requirements.
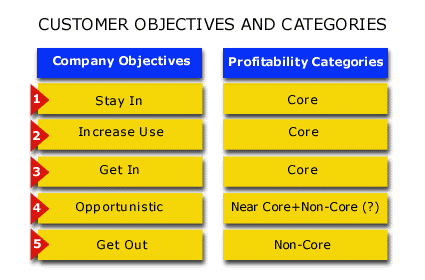
The Company should set specific objectives for each customer in these customer categories. The objectives are:
-
Stay In the relationship, with the same proportions of the customer’s purchases that the Company currently serves.
-
Increase Use, where the Company would like a current customer to purchase a higher proportion of its needs from the Company
-
Get In, where the Company would like to enter a customer relationship it does not have today
-
Opportunistic service, where the Company will serve the customer only if it has excess available capacity for a period of time
Get Out, where the Company plans to withdraw from the customer relationship.
Why:
This classification becomes the framework around which the Company develops its sales and marketing programs, its responses to customer requests and its program for product and service innovation.
What to Watch For:
If a company is already a Primary Supplier of a major customer, delivering more than 80% of that customer’s purchases, it may choose to treat that customer with a “Stay In” objective. The company must consider whether it really wants to own 100 percent of the purchases of a significant customer. In the case of 100 percent ownership, customers, especially Intermediary Customers, may blame their sole supplier for many of their own failures and poor profits and demand even lower prices.
Opportunistic customers may generate contribution from the use of capacity the company otherwise would hold, unused, for anticipated and unanticipated growth among its Core customers. This happens in Hostile markets.
In a Hostile marketplace, a company may choose to serve Non-Core customers in order to use capacity that otherwise would generate cash but no contribution to returns. However, the company would not add to its existing capacity without first using all the capacity supporting Non-Core and perhaps even Near-Core customers.
-
In a Hostile market, specific customers of each size (i.e., Very Large, Large, Medium and Small) may be Non-Core Opportunistic customers, even if the size/role segment would normally be a Core customer segment, because their individual pricing is low. Often, the pricing differences to customers within a size category will have a greater variation than the differences in average prices across the customer size categories.
The industry’s leading customers may create an industry leader effect. This effect makes the apparent low profitability on some of these big customers into Core customer relationships.
A price-based relationship is usually an indication of a Non-core customer. The low prices in these relationships may radiate to other customers and result in a loss of cash on the relationship.
In an ideal situation, Core customer volume would make up 100% of the company’s sales. Percentages below 67% may signal impending trouble.
-
The Core customers with the lowest costs of Get-In or Increase Use are those served by weak competitors.
Action:
The Company would focus its resources on developing, first, a superb value proposition for the Core customers and, second, programs to convert Near-core customers into Core customers. The Company would serve some Near-core and Non-core customers, but only if it had unused capacity available for a period of time and if the sales to the customer would produce cash for the Company.
More Information on Final Targets on the Advanced Site >>
For helpful context on this step:
Videos:
-
Video #54: Cost Reduction By Winners vs. Losers in Hostility
-
Video #65: Core Customers Part 3: Developing Plans for Core Customers
Perspectives:
Symptoms and Implications:
